Hip Replacement Surgery
Home > Health Info > Health Articles
Hip replacement surgery is a procedure performed to remove the damaged, necrotic, or fractured parts of the original hip joint and replace them with an artificial hip joint (Prosthesis). The goal is that most closely resembles the natural motion of a real joint.
Causes of Chronic Hip Pain
Common causes of chronic hip pain include avascular necrosis of the femoral head, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
- Avascular necrosis is a condition which the femoral head loses its blood supply, head leading to bone collapse. It is commonly found in individuals aged 30-40 years. Causes include alcohol consumption, prolonged steroid use, hip dislocation or fracture, and radiation exposure to the hip area.
- Osteoarthritis usually occurs in patient over 50 years old and often has family history of osteoarthritis. Sometimes it may be caused by congenital irregular of the joint surfaces. When uneven hip surfaces rub together, it leads to pain and restricted movement.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the joint lining, causing non-infectious inflammation. It can affect multiple joints throughout the body, with symptom that flare up and subside over time, it commonly affects finger joints cause progressive joint damage.
- Post Traumatic Arthritis occurs after an injury or fracture near the hip joint. The articular surface may be damaged, or blood supply to the femoral head may be compromised, eventually resulting in hip degeneration.
- Femoral neck fracture can occur at any age but is more common among the elderly, especially those with osteoporosis who experience a fall or impact to the hip.
- Congenital Hip diseases are hip degeneration may develop later in life as a result of developmental abnormalities of the hip joint that occurred during childhood.
When Hip Replacement Surgery is Needed
The decision to undergo hip replacement surgery should be made collaboratively between the patient, patient’s family, and the orthopedic surgeon. Most patients requiring hip replacement surgery are between 60-80 years old. The Indications for surgery depends on several factors – such as the severity of the disease, the level of pain experience, the degree of disability, and the patient’s overall health condition. The physician will evaluate each case individually to determine whether surgery is appropriate and discuss the best treatment plan with the patient and their family.
Indications for Hip Replacement Surgery
- Severe hip pain that limits daily activities such as walking or bending of hip.
- Persistent hip pain at rest, both day and night
- Hip stiffness that limits movement or the ability to lift the leg
- Minimal or no improvement despite full medical treatment, physical therapy, and the use of walking aids
- Severe adverse effects or complications from long -term medication use
- Hip fractures unsuitable for treatment with metal fixation methods
- The need for modern, muscle-sparing hip replacement techniques
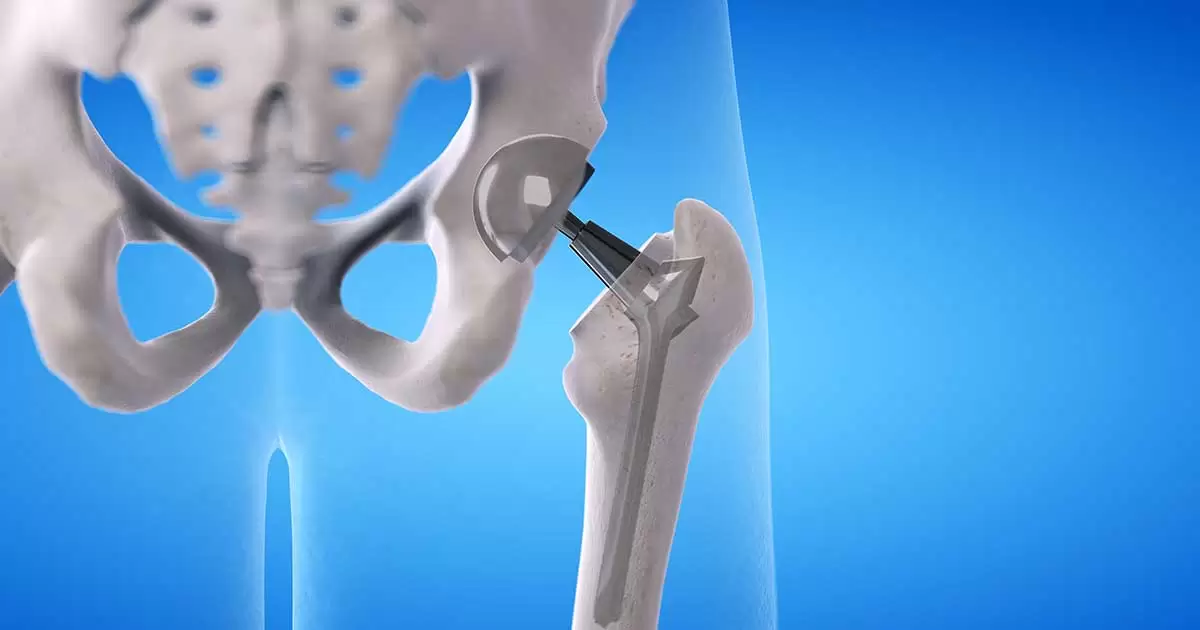
Components of an Artificial Hip Joint
An artificial hip joint has 4 main components:
- Acetabular cup (artificial hip socket) – made of metal, fixed to the hip socket in the pelvic bone
- Acetabular liner – made of special plastic, serves as the contact surface with the artificial femoral head
- Femoral head – A metal sphere designed to replicate the natural femoral head
- Femoral stem – A metal component inserted into the upper femur to support the artificial joint
Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
Modern hip replacement offers several advantages:
- Significant reduction of hip pain
- Faster recovery due to muscle-sparing surgical techniques
- Smaller surgical incision
- More precise implant positioning during revision surgery
- Low risk of hip dislocation
- Real-time X-ray verification of implant position during surgery
- Use of computer navigation systems for accurate alignment
- Easy postoperative assessment to ensure equal leg length
Contraindications and Precautions
- Active infectious arthritis with ongoing inflammation
- Severely weak hip muscles that increase the risk of dislocation
- Neurological or muscular diseases affecting hip stability
- Blood or vascular diseases with high complication risk
- Severe osteoporosis in the hip area
- Severely obesity
Conclusion
The primary purpose of hip replacement surgery is to relieve pain caused by degenerative joint disease and restore mobility. After surgery, patients can walk normally without pain, move the hip joint freely, and regain proper leg length.
Hip replacement provides the best results for patients with severe joint damage or deformity, helping them return to comfortable movement and improving their overall quality of life.
For more information please contact : Orthopedic Center
Share :