Hair Loss
Главная > Информация о здоровье > Статьи о здоровье

Hair Loss
Hair loss refers to the loss of hair on the scalp or any part of the body. The severity can vary, and it may be observed in the following ways:
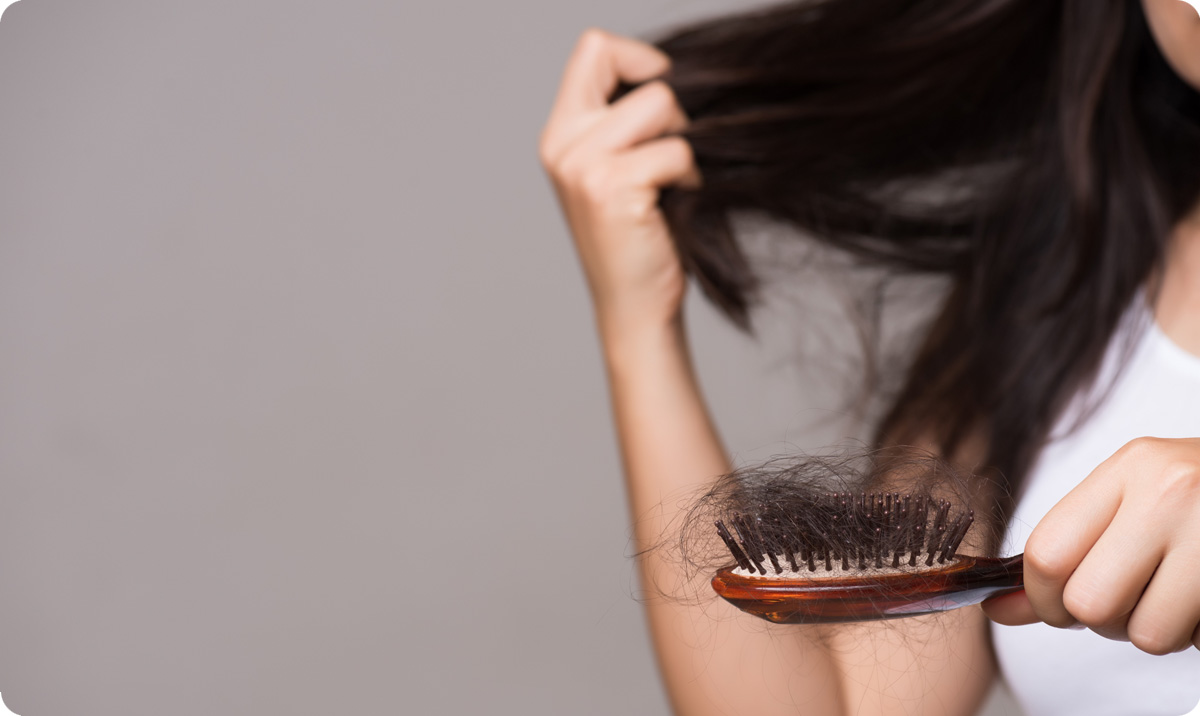
- Seeing a large amount of hair in the drain after washing your hair
- Finding clumps of hair on the brush, pillow
- Noticing thinning hair or bald patches, reduced hair density at the crown, or a receding hairline
These signs indicate excessive hair loss and it’s advisable to consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
When is hair loss considered abnormal?
- Losing more than 70-100 hairs per day for those who wash their hair almost daily, or more than 200 hairs per day for those who wash their hair every 3-4 days.
- Hair loss during washing or drying in small amounts is normal. However, losing over 70-100 hairs per day during daily activities (e.g., on the pillow after waking, during meals, cooking, working) is considered abnormal.
- Patchy hair loss, where hair falls out and forms small coin-sized patches.

Causes
- Genetic Predisposition: The most common cause is a family history of baldness. Studies suggest that genetic and environmental factors like stress and pollution can trigger hair thinning, which is linked to the male hormone androgen.
- Stress, Illness, or Surgery: Long-term fever, childbirth, psychological stress, rapid weight loss, etc.
- Side Effects of Medications: For cancer, hypertension, arthritis, depression.
- Drug Allergies
- Radiation Therapy
- Infections: Fungal infections, syphilis, HIV, herpes.
- Skin Diseases: DLE and autoimmune diseases like SLE.
- Hormonal Issues: Thyroid problems, high or low hormone levels.
- Scalp Infections and diseases causing scarring, like lichen planus and certain types of lupus, can cause permanent hair loss.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, childbirth, stopping birth control pills, menopause.
- Stressful Events: Surgery, illness, or psychological trauma can cause temporary hair loss, which usually regrows without treatment.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of protein, iron, and other nutrients.
- Hair Damage: Tight hairstyles, hair rollers, ponytails, and braiding close to the scalp.
- Psychological Disorders: Twisting, pulling, or breaking hair due to psychological issues.

Diagnosis
Doctors will conduct a physical exam, inquire about medication use, and medical history of the patient and their family. Additional diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: To identify other causes of hair loss.
- Pull Test: To see how much hair comes out when gently pulled.
- Scalp Biopsy: Examining a scalp tissue sample under a microscope to determine the cause of hair loss.
Treatment
- Medication: Initial treatment often involves topical or oral medications prescribed by a specialist due to possible side effects.
- Hormonal Adjustment: For hair loss due to hormonal deficiencies.
- PRP Injection: Injecting platelet-rich plasma to stimulate stem cells in the hair roots.
- Laser Therapy: To address hair deterioration and strengthen hair roots.
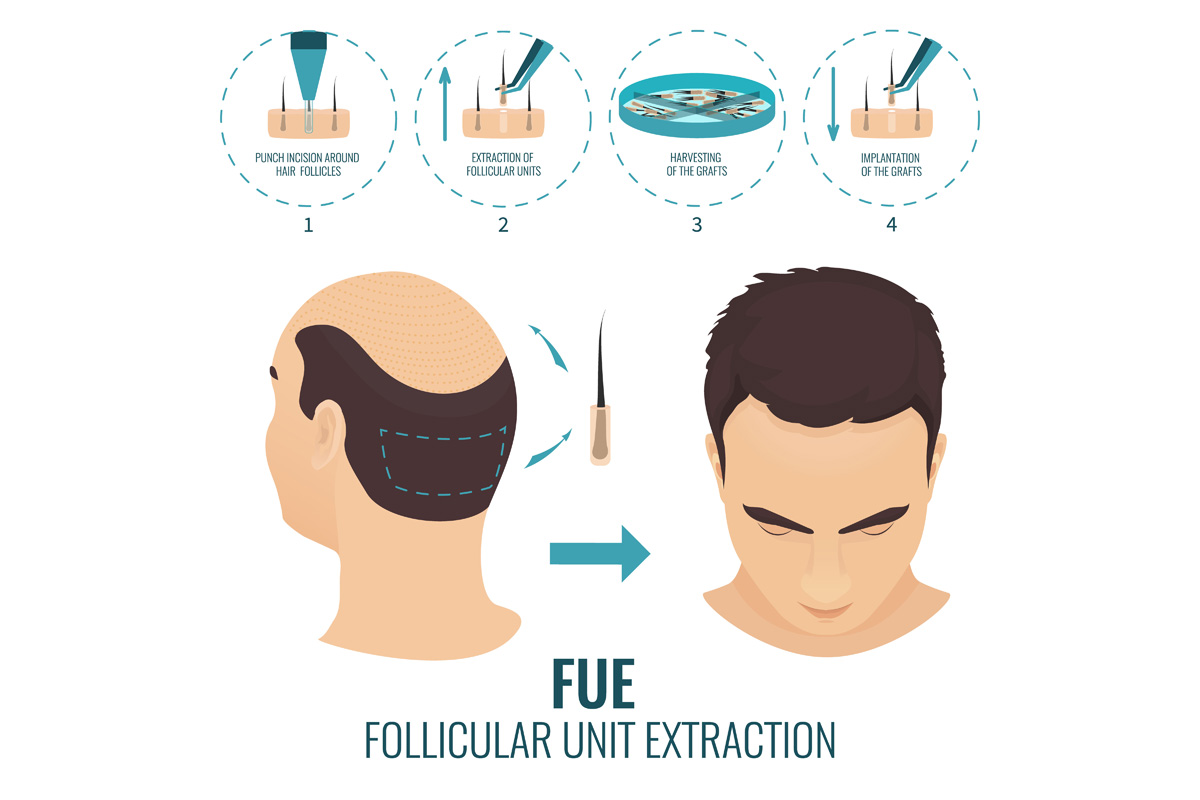
- Hair Transplant: Transplanting hair roots from unaffected areas to bald areas via surgery.
Prevention
Preventing hair loss involves daily self-care and the use of specialized products or treatments:
Daily Self-Care:
- Balanced Diet: Include vitamins that nourish hair, like iron, zinc, vitamin D, B1, B3, B7 (biotin), and B12.
- Avoid Stress: Stress can increase hair loss; engage in stress-reducing activities like exercise, meditation, or sufficient rest.
- Avoid Hair Damage: Minimize the use of high heat on hair, such as blow dryers, straighteners, or frequent perming.
- Limit Hair Coloring: Avoid frequent chemical treatments, especially combined straightening, perming, and bleaching.
- Proper Hair Washing: Avoid very hot water and brushing wet hair.
- Maintain Scalp Hygiene: Regularly wash hair with suitable products that do not cause allergies, itching, dandruff, or scalp rashes.
- Scalp Massage: Gentle massage can improve blood circulation and promote hair growth.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Do not pull, twist, or rub hair excessively.
Specialized Products and Treatments:
- Shampoos and Conditioners: Use products designed to prevent hair loss or promote hair growth.
- Medications and Supplements: Supplements like biotin, minoxidil for hair loss issues.
- Laser Therapy: Low-Level Laser Therapy to stimulate hair growth.
- Hair Transplantation: For severe hair loss or baldness.
Daily hair and scalp care is crucial for preventing hair loss. If excessive hair loss occurs, consulting a doctor to determine the cause and appropriate treatment is advisable.
Post Views: 168
Предоставить общий доступ :




